What's New
Displaying results 1051 - 1060 of 4924

Resource | Publications,
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3 – ensuring health and well-being for all at all ages – is critical to achieving progress on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Because health is an integral part of human capital and a precondition, driver and outcome of sustainable development, SDG 3 is linked to around 50 health-related targets across the SDGs and the pledge to leave no one behind. The overall objective of the Global Action Plan is to enhance collaboration among 12 global organizations engaged in health, development and humanitarian responses to accelerate country progress on the health-related SDG targets. The Plan presents a new approach to strengthening collaboration among and joint action by the organizations, building on an initial joint commitment made in October 2018. The Plan is primarily intended to be strategic but provides some operational detail to guide implementation while also allowing flexibility for adjustment based on regular reviews of progress and learning from experience.

Resource | Guidelines,
One important way to mobilise more resources and achieve a greater programmatic impact is by harnessing the full range of assets, capacities and innovations business has to offer – whether they be financial, technical or institutional.

Resource | Publications,
This report complements the evaluations of hepatitis responses conducted by fellow stakeholders. One particular inspiration was the WHO’s recent development of country response profiles through a survey on a checklist of indicators of structure (e.g., policy decisions), input (e.g., budget allocation) and process (e.g., implementation of WHO guidelines). To complement the WHO’s top-down macro-level overview of HCV responses, the Coalition PLUS survey provides a bottom-up micro-level evaluation of the HCV response at selected sites in five middleincome countries: India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Morocco, and Thailand. As an explanatory and qualitative survey, the findings and recommendations serve to inform the response in the countries involved in the study.

Resource | Publications,
Asia-Pacific is the most disaster-prone region in the world and home to a number of long-running conflicts. The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) places women and girls at the centre of humanitarian response. This publication shares examples of how we support actions to better mitigate the risks of disasters and support humanitarian response work that is underpinned by UNFPA’s unique mandate encompassing sexual and reproductive health, gender equality, population data and youth empowerment.

Resource | Publications,
In line with UNDP’s ‘Strategic Plan 2018–2021’ and ‘HIV, Health and Development Strategy 2016–2021: Connecting the Dots’, UNDP contributes to UHC. This UNDP Issue Brief on ‘Universal Health Coverage for Sustainable Development’ outlines UNDP’s contributions toward supporting countries to remove barriers to health and improve the affordability, accessibility and quality of health care and systems.

Resource | Infographics,
Girls and women make up more than half of the 37.9 million people living with HIV. Ending AIDS by 2030 requires that we address girls’ and women’s diverse roles by putting them at the centre of the response.
Resource | Infographics,
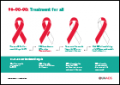
There are 37.9 million people living with HIV. 79% know they are HIV-positive. The rest do not. Three out of five people living with HIV are on antiretroviral therapy. Only 53% of people living with HIV have undetectable levels of the virus.

Resource | Publications,
States have a moral and legal obligation—under the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, human rights treaties, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and other international obligations—to remove discriminatory laws and to enact laws that protect people from discrimination.

Resource | Publications,
Microbes do not stop at national borders, so an infectious disease threat anywhere is a threat everywhere. Making our world safer from epidemics means strengthening the capacity of countries to prevent, detect and respond effectively to current and emerging health threats.

Resource | Publications,
Robust health systems are not only essential to ending HIV, TB and malaria as epidemics, they yield broader health outcomes, delivering health services in a sustainable, equitable and effective way. Resilient and sustainable systems for health are necessary for accelerating progress toward universal health coverage, and help countries prepare for emerging threats to global health security.





